Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Koyama, Tomohiro*; Ieda, Junichi; Chiba, Daichi*
Applied Physics Letters, 116(9), p.092405_1 - 092405_5, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:25.92(Physics, Applied)Koyama, Tomohiro*; Nakatani, Yoshinobu*; Ieda, Junichi; Chiba, Daichi*
Science Advances (Internet), 4(12), p.eaav0265_1 - eaav0265_5, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:88.54(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We show that the electric field (EF) can control the magnetic domain wall (DW) velocity in a Pt/Co/Pd asymmetric structure. With the application of a gate voltage, a significant change in DW velocity up to 50 m/s is observed, which is much greater than that observed in previous studies. Moreover, a DW velocity exceeding 100 m/s is clearly modulated. An EF-induced change in the interfacial Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (DMI) up to several percent is found to be the origin of the velocity modulation. The DMI-mediated velocity change shown here is a fundamentally different mechanism from that caused by EF-induced anisotropy modulation. Our results will pave the way for the electrical manipulation of spin structures and dynamics via DMI control, which can enhance the performance of spintronic devices.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Kurita, Genichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Sakurai, Shinji; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(3), p.2281 - 2285, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)High performance steady-state operation for JT-60SC are evaluated by the TOPICS analysis. 

 5 and bootstrap current fraction
5 and bootstrap current fraction  86% is kept steady at I
86% is kept steady at I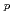 =1.5 MA, B
=1.5 MA, B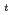 =2 T by neutral beam power of 11 MW. The ERATO-J analysis shows that the external-kink mode with multiple toroidal mode numbers of n=1 and n=2 is stable at
=2 T by neutral beam power of 11 MW. The ERATO-J analysis shows that the external-kink mode with multiple toroidal mode numbers of n=1 and n=2 is stable at 

 5.5 at the average ratio of conducting wall radius to plasma minor radius of about 1.2 with the wall stabilisation effect. Resistive wall modes, induced by a close location of the wall to plasma, is expected to be suppressed by the active feedback stabilisation with a set of non-axisymmetric field coils behind the stabilising plates. Further optimisation for the high-
5.5 at the average ratio of conducting wall radius to plasma minor radius of about 1.2 with the wall stabilisation effect. Resistive wall modes, induced by a close location of the wall to plasma, is expected to be suppressed by the active feedback stabilisation with a set of non-axisymmetric field coils behind the stabilising plates. Further optimisation for the high-
 accessibility by the plasma shaping is performed with the TOSCA analysis. The plasma shaping factor defined as S=(I
accessibility by the plasma shaping is performed with the TOSCA analysis. The plasma shaping factor defined as S=(I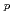 /aB
/aB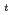 )q
)q
 and strongly correlated to the plasma elongation and triangularity, is scanned from
and strongly correlated to the plasma elongation and triangularity, is scanned from  4 to
4 to  6, which extends the availability of current and pressure profile control for the high performance plasma operation.
6, which extends the availability of current and pressure profile control for the high performance plasma operation.
Konovalov, S. V.; Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Tsypin, V. S.*; Galv o, R. M. 0.*; Nascimento, I. C.*
o, R. M. 0.*; Nascimento, I. C.*
Plasma Physics Reports, 29(9), p.779 - 784, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.11(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The problem of drift stabilization of internal resistive-wall modes (RWMs) in tokamaks is theoretically investigated. The basic assumption of our model is that these modes are unstable in the absence of a conducting wall and stable in the presence of a close-fitting ideally conducting wall, when drift effects are neglected. Stability of the internal RWMs, was estimated for several existing tokamaks contributing to the ITER data base, namely, AUG (ASDEX-Upgrade), DIII-D, JET, TFTR and JT-60U, as well as for the projected ITER-FEAT. It is concluded that although drift effects do not stabilize the internal RWMs in current devices, they should be effective for suppressing these modes in reactor-grade tokamaks.
J.Pulpan*
JAERI-M 93-115, 15 Pages, 1993/06
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Makoto; *; Wu, Y.*; *; Uritani, Akira*; Mori, Chizuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 330, p.158 - 164, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:66.94(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
; ; ; ;
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 256, p.333 - 338, 1987/00
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:87.75(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
; Murao, Yoshio
JAERI-M 83-090, 86 Pages, 1983/06
no abstracts in English
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 20(5), p.389 - 399, 1983/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:35.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Murakami, Yoshio; ; ; *
JAERI-M 8513, 40 Pages, 1979/10
no abstracts in English